dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is a technology that allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of light. This article will explore the advantages of DWDM and its various components.
The Benefits of DWDM
DWDM offers several advantages in terms of increased bandwidth, improved scalability, and cost-effectiveness. By utilizing multiple wavelengths, DWDM significantly increases the capacity of an optical fiber network. It enables the transmission of numerous data streams simultaneously, allowing for efficient utilization of available resources.
In addition to increased bandwidth, DWDM also provides enhanced scalability. With traditional systems, adding more capacity would require laying additional fibers or upgrading existing ones. However, with DWDM technology, new channels can be added simply by assigning unused wavelengths without any physical modifications to the infrastructure.
Furthermore, implementing DWDM can lead to cost savings for network operators. Instead of investing in new fibers or equipment upgrades every time there is a need for additional capacity, they can leverage the existing infrastructure and maximize its potential through wavelength multiplexing.
The Role of Optizone Technology
Optizone Technology is an essential component within a DWDM system that helps optimize signal quality and minimize power loss during transmission. It ensures that each channel’s wavelength remains stable throughout the entire network by compensating for variations caused by temperature changes or other factors.
This technology utilizes advanced techniques such as dynamic gain equalization and dispersion compensation to maintain optimal performance across all channels within the system. By mitigating signal degradation issues like chromatic dispersion and polarization mode dispersion effectively, Optizone Technology plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable data transmission over long distances.
Fiber Optic Isolators in DWDM
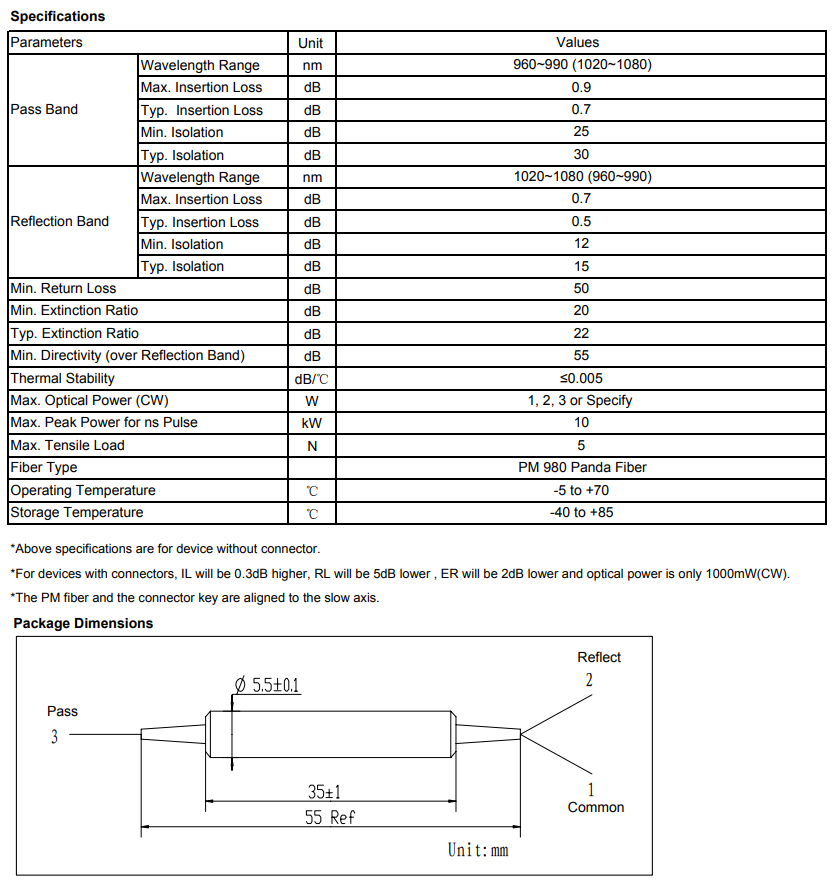
fiber optic isolators are another important component of a DWDM system. These devices prevent unwanted reflections and backscattering of light, which can degrade the quality of transmitted signals. By isolating each channel from one another, fiber optic isolators help maintain signal integrity and minimize crosstalk.
Additionally, fiber optic isolators also provide protection to sensitive optical components within the network by preventing any feedback that could potentially damage them. They act as barriers between different sections of the system, ensuring that disturbances or failures in one part do not affect others.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) offers significant advantages for optical fiber networks. It enables increased bandwidth capacity, improved scalability without physical modifications, and cost savings through efficient resource utilization. Optizone Technology optimizes signal quality and stability within a DWDM system, while fiber optic isolators protect against signal degradation and ensure overall network reliability. With these advancements in technology, DWDM continues to play a crucial role in meeting the ever-growing demand for high-speed data transmission.
